리소스 더 보기
Your customers can tell you what they like and what they’ll buy, but they can’t always explain why they choose one brand over another. Unless they are marketers themselves, they may not fully understand the role of price, brand image, packaging, brand name, promotions, and advertising in their decision to purchase.
Choice modeling, a type of preference structure modeling, is a powerful tool for understanding what drives customer interest and purchase decisions. It’s considered to be the most scientifically robust way to discover and understand how customers make choices.
Let’s take a closer look at choice modeling and how it can fit into your marketing strategy.
What is choice modeling?
Choice modeling is an analytical method that is used to simulate consumer shopping behavior.
Research participants are unaware of what is being measured as they are presented with visual choices with marketing variables such as advertising, pricing, packaging, features, etc. Participants are asked to make trade-offs among the provided options, ultimately choosing what they value most from those options.
Inferences drawn from participant decisions are used to predict the likelihood of a customer choosing one product or feature over another.
The data provides deeper insights into what is important to your target market, allowing you to make insightful, data-driven business decisions for various dilemmas, including:
- Price setting for profitability
- Bundling features
- Product positioning
- Viability of a concept
- Media effectiveness
- Promotions
- Advertising messages
- Packaging
Advantages of choice modeling
The most significant advantage of choice modeling is that it provides deeper insight into your target market’s values. Other advantages include:
- Respondents must consider trade-offs between attributes revealing the most valued attributes
- Definitive frame of reference through a predetermined array of attributes and alternatives
- Enables prices to be estimated for each attribute by assigning value
- Identify an optimal mix of features to create a product your target market would deem valuable and the price they are willing to pay
- Can be used in most cases for a hard estimate of current and future preferences
Limitations of choice modeling
As with any research method, there are limitations to be considered. These limitations include:
- Discrete choices only provide ordinal data
- A large amount of data is required to assure statistical significance
- Cost and time may be higher than other methods
How does choice modeling work?
Choice modeling says that individuals make decisions based on weighing the utility of each alternative—choosing the option with the highest utility. This is accomplished using the logistic statistical model to determine the probability of future events.
There are three main steps to choice modeling:
- Identify your product’s key factors: This is most effectively accomplished via focus groups. You can explore consumer buying motivations and impressions of your product or service with a trained facilitator. With that information, you can develop hypotheses about the key factors that influence their choices.
- Test your hypotheses: In this step, you’ll use surveys in one of two ways. First, for existing products, you can survey your target market to find out what they usually buy or have purchased in the past in your product category.
The second option is to present survey participants with a set of choice experiments. Each experiment presents a hypothetical marketplace that contains a set of products. The products are described, and the participants are asked what they would do in terms of purchasing—buy a product, not buy anything, or buy later. Additional experiments vary pricing and other product characteristics, and participants make choices each time based on the new information.
- Statistical analysis: Analyze your collected data to draw inferences, identify trends, and generate insights about what your target market values most.
Types of choice modeling
There are four main types of choice modeling analysis. The type you use depends on your technological knowledge and what type of data and insights you are seeking.
R-Language choice modeling
R is a free, open-source programming language created by statisticians for working with data. R-Language is frequently used to analyze large datasets with complex variables. R can handle both discrete (nominal or ordinal) and probabilistic variables. It runs on a wide variety of UNIX platforms, Windows, and Mac OS. R can be used for statistical analysis and visualization of your SurveyMonkey data. R is known for being difficult to learn for those with limited experience in programming.
Conjoint analysis
Another type of choice modeling is conjoint analysis, also known as trade-off analysis. Conjoint analysis is based on the concept that any offering from a company can be broken down into a set of attributes that impact a customer’s perceived value of the offering.
Use conjoint analysis to determine the most influential attributes on a survey participant’s decision to purchase.
Your survey structure for conjoint analysis should ask participants to rank the importance of specific attributes or to choose between different combinations of features and prices.
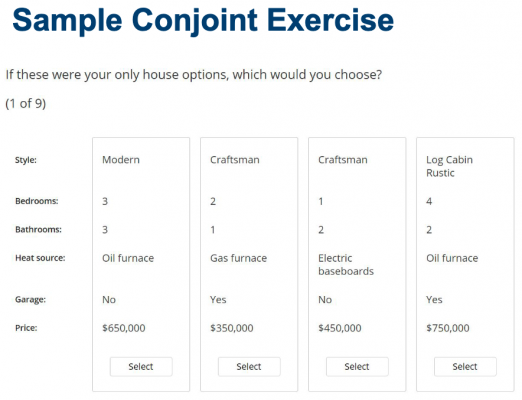
During analysis, a value is assigned to each attribute. The data can then be used to decide the combination of features that will be most attractive to customers and at what price they are willing to make a purchase.
Discrete choice modeling
Yet another method of determining the probability that a consumer will choose a particular alternative is discrete choice modeling. This is best for product categories that see one purchase used over a long period of time or products that have many features, such as smartphones.
In discrete choice modeling, both current and potential customers are asked to view a realistic scenario that includes all of the competing products in the marketplace. They are then presented with varying combinations of marketing strategies and asked which product they would purchase based on that marketing.
Volumetric choice modeling
Volumetric choice modeling is common for businesses in product categories that experience multiple product purchases in short amounts of time and where repeat purchase volume is important. In this type of modeling, current and potential customers are provided with a realistic shopping scenario that includes all of the competing products in the particular marketplace. They are asked to indicate how many of each product they would buy. This reveals the role and importance of marketing variables in a situation where varying quantities of multiple brands can be purchased.
Is choice modeling in your marketing toolkit?
Choice modeling effectively determines what’s important to your customers and potential customers when making purchase decisions. Start using choice modeling today to test product features for implicit value, the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, set pricing structures, and more.
SurveyMonkey has a variety of market research services available, including product optimization, price sensitivity analysis, and survey design. Explore all of our market research solutions to optimize your marketing campaigns and brand success.
Get started with your market research
Global survey panel
Research services
Expert solutions
To read more market research resources, visit our Sitemap.